What is testosterone and what does testosterone do?
Abstract
Testosterone is a crucial steroid hormone primarily secreted by the male testicles and female ovaries, with levels in men being about ten times higher than in women. In adult males, serum testosterone levels typically range from 14 to 25.4 nmol/L, while in females, they range from 1.3 to 2.8 nmol/L. This hormone plays essential roles in various body functions, particularly in men.
The effects of testosterone can be categorized into anabolic (growth-promoting) and masculinizing effects. Here are the key physiological impacts:
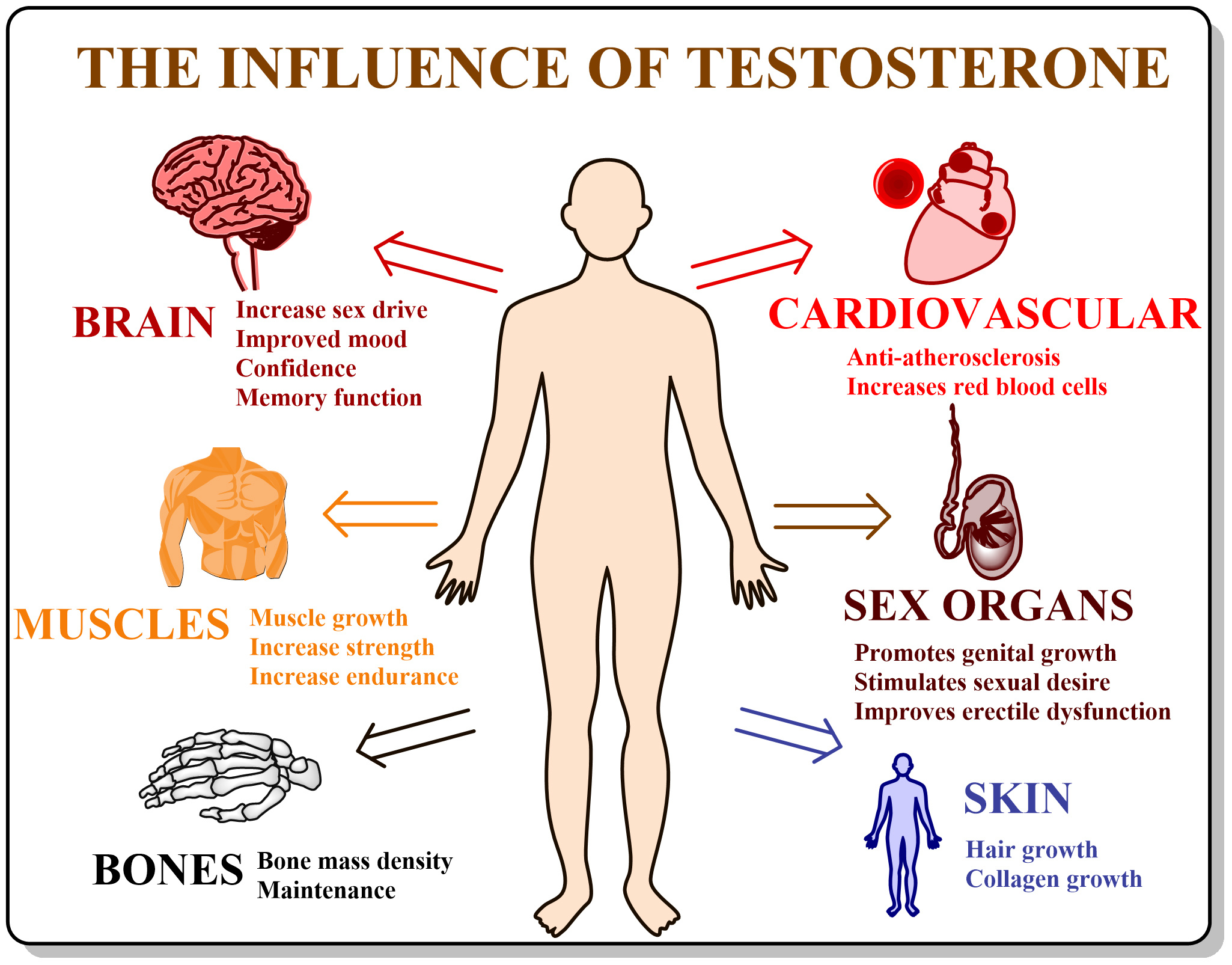
1. Brain: Testosterone influences brain development during embryonic and infant stages and promotes the structural formation of the brain during adolescence.
2. Muscle: It enhances muscle development, increases strength, and reduces body fat.
3. Bones: Testosterone helps prevent osteoporosis and fractures by stimulating bone cell formation.
4. Cardiovascular System: It exhibits anti-atherosclerotic effects, potentially lowering the risk of coronary heart disease and helping to manage blood lipids and glucose levels.
5. Reproductive System: Testosterone promotes genital growth, stimulates sexual desire, enhances sexual satisfaction, and can improve erectile dysfunction.
6. Skin: It encourages the growth of facial and body hair and stimulates sebaceous gland activity.
These diverse effects highlight the importance of testosterone in maintaining overall health and well-being, especially in men.
Be related to


