What we can expect T999 do
Enhance Exercise Performance
1. Mouse Weighted Swimming Test
An experiment on mice (weighing 18-22 g) showed that feeding mice with T999 at low, medium and high doses of 0.82 mg, 1.64 mg and 2.46 mg per day for 7 days (equivalent to a daily dose of 200 mg, 400 mg and 600 mg for a 60 kg human) could extend the swimming time of mice by 17.7%, 37.1% and 61.5%, respectively, corresponding to the increasing doses.
Table 2 Effects of T999 on the weight-bearing swimming test in mice(X±SD, n=10)
|
Group |
Dose (g/kg) |
Swimming time/min |
|
Control |
Equal volume of H2O |
6.2±1.8 |
|
TFG-HD |
0.123 |
10.2±4.5** |
|
TFG-MD |
0.082 |
8.5±1.7** |
|
TFG-LD |
0.041 |
7.3±2.7 |
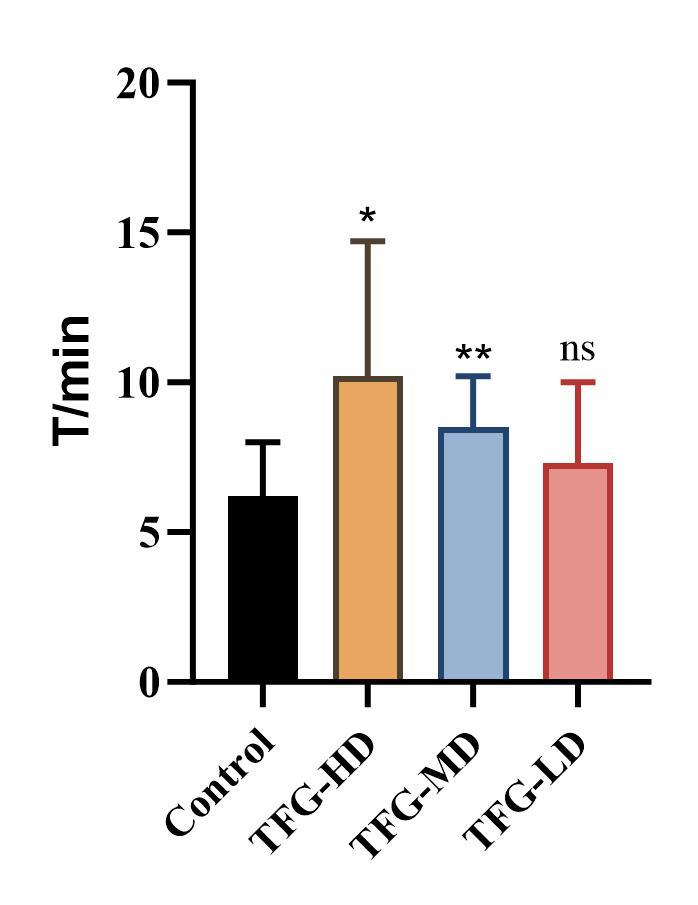
Fig.3 Effect of T999 on the weight-bearing swimming test in mice
Note: *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with the blank control group.
Experimental Institution: Hunan Key Laboratory of Small Molecule Drug Discovery and Translation for Chronic Disease Diagnosis and Treatment.
Experimental Conditions:
1.1. Animal Selection
Forty clean-grade adult male mice (weighing 18-22 g) were randomly divided into four groups.
1.2. Drug Administration
For seven consecutive days, the mice received drug administration via gavage once daily.
1.3 . Weight Loading
On the seventh day, 60 minutes after the gavage, alloy blocks weighing 10% of each mouse's body weight were attached to their tails.
1.4 . Swimming Test
The mice were placed in a swimming bucket, and the time taken from the start of swimming until they sank due to exhaustion was recorded.
This experimental design enables the assessment of the effects of the administered drug on swimming endurance and overall physical performance in the mice.
2. Mouse Hypoxia Tolerance Experiment
An experiment on hypoxia tolerance in mice revealed that after 7 days of daily feeding with T999 at low, medium, and high doses (equivalent to 200 mg, 400 mg, and 600 mg for a 60 kg human), breathing time was extended by 25.2% and 32.2% at the medium and high doses, respectively, compared to the blank control group. This finding indicates that T999 has a significant hypoxia tolerance effect in hypoxic mice, suggesting its potential benefits for activities in hypoxia-prone sports such as mountaineering and diving in high-altitude areas.
Table 3 Effects of T999 on hypoxia tolerance at normobaric pressure in mice(X±SD, n=10)
|
Group |
Dose (g/kg) |
Respiratory arrest time /min |
|
Control |
Equal volume of H2O |
14.3±2.1 |
|
T999 high dose group |
0.123 |
18.9±1.9** |
|
T999 medium dose group |
0.082 |
17.9±2.0** |
|
T999 low dose group |
0.041 |
17.6±3.1* |
Note: *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with the blank control group.
Experimental Institution: Hunan Key Laboratory of Small Molecule Drug Discovery and Translation for Chronic Disease Diagnosis and Treatment.
Experimental Conditions:
2.1 . Animal Selection
Forty clean-grade adult male mice (weighing 18-22 g) were randomly divided into four groups, with 10 mice in each group.
2. 2. Drug Administration
● The mice received intragastric administration once daily for 7 consecutive days.
● The blank control group was given an equal volume of purified water.
2.3. Isoproterenol Injection
On the seventh day, one hour after administration, isoproterenol hydrochloride was injected intraperitoneally into each mouse.
2.4. Breathing Time Measurement
● After a specified period following the injection, the mice were placed in a sealed wide-mouth bottle containing soda lime, with Vaseline applied to the bottle mouth to create a seal.
● Once the mice were inside the bottle, it was sealed, and the breathing time of each mouse was recorded using a stopwatch.
This experimental setup allows for the evaluation of respiratory function under the influence of isoproterenol, providing insights into the effects of the treatments on breathing capacity.
3. Fruit Fly Crawling Experiment
An experiment on aging fruit flies demonstrated that the movement ability of aging fruit fly W118 in the blank control group was reduced compared to young fruit flies. However, when the aging fruit flies were cultured with the drug T999, their movement ability significantly improved (p < 0.01) compared to the blank control group. Specifically, T999 at a concentration of 0.05 g/L prolonged the crawling movement time of male aging fruit flies by 49.8%.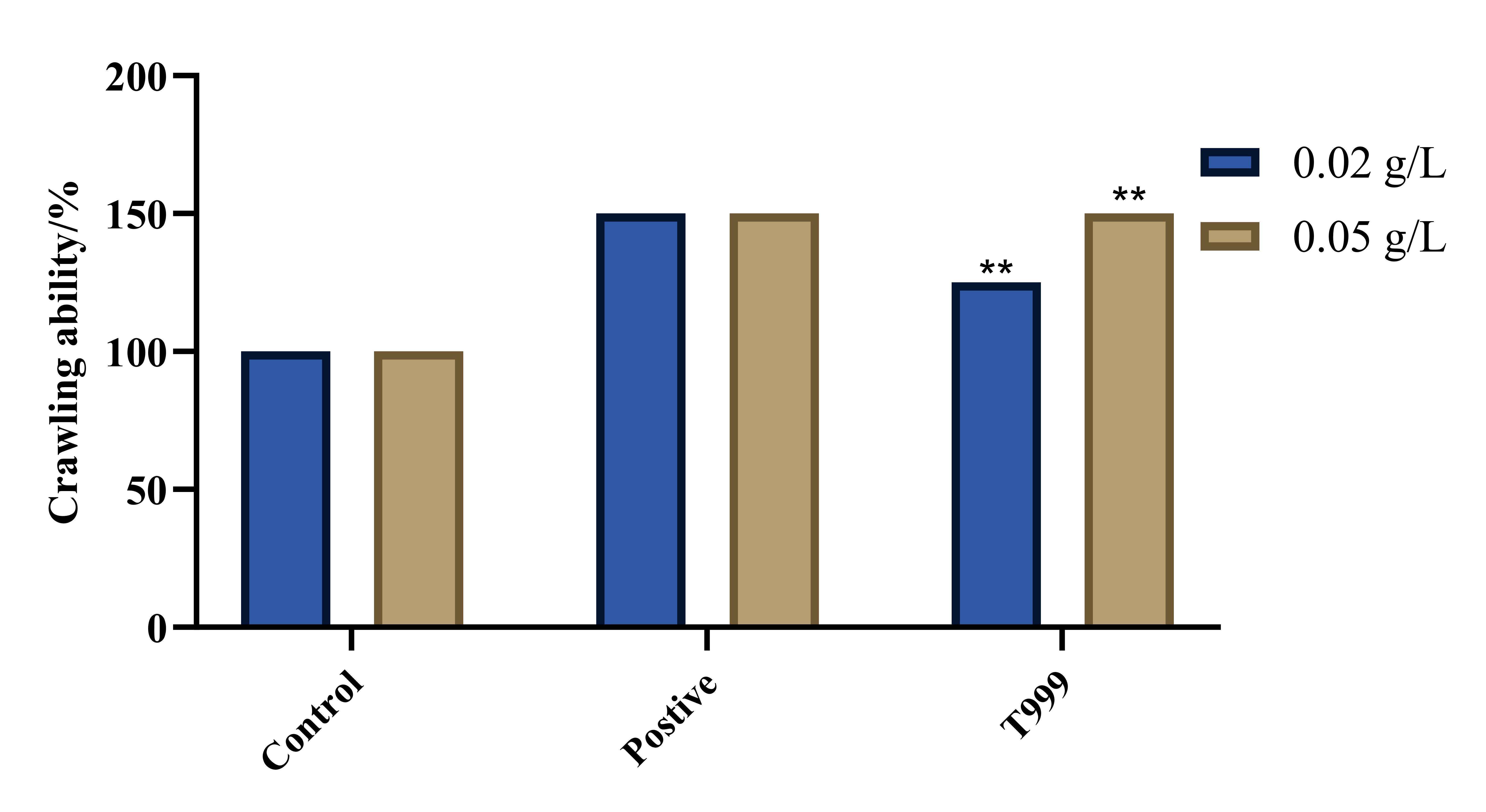
Fig. 4 Effect of T999 on the crawling ability of male fruit flies (**P<0.01 VS blank control group)
Experimental Institution: Hunan Key Laboratory of Small Molecule Drug Discovery and Translation for Chronic Disease Diagnosis and Treatment.
Experimental Conditions:
3.1. Selection of Drosophila
Select several wild-type Drosophila melanogaster W118.
3.2. Preparation of Culture Media
● Prepare drug-containing culture media by adding T999 at concentrations of 0.02 g/L and 0.05 g/L.
● For the blank control group, use a 20% sucrose solution.
● For the positive control group, select young fruit flies and also add a 20% sucrose solution.
3.3. Culture Period
Culture the fruit flies in their respective media for 3 days.
3.4. Transfer to Observation Setup
● After 3 days, transfer the fruit flies to a normal food group.
● Place them in a transparent cylinder marked 8 cm from the bottom.
3.5. Experimental Procedure
● Use 80 to 100 fruit flies in each group.
● At the start of the experiment, gently tap the cylinder to settle the fruit flies to the bottom.
● Count the number of flies that climb to the marked line within 10 seconds.
3.6. Repetitions and Data Calculation
● Repeat the experiment 10 times for each group.
● Calculate the average number of flies that reached the mark within 10 seconds for each group.
This setup assesses the climbing ability of Drosophila melanogaster in response to T999, providing insights into its effects on locomotor activity.


